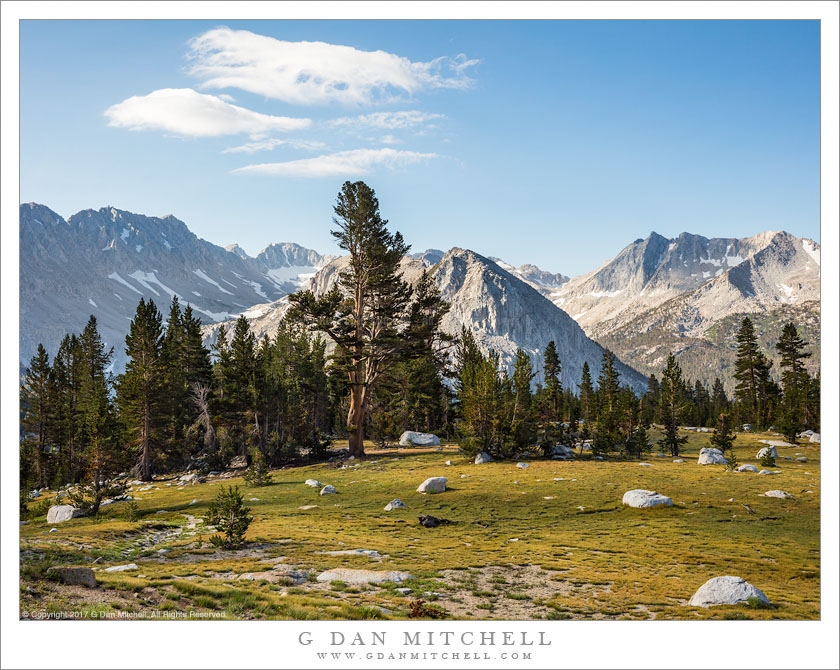
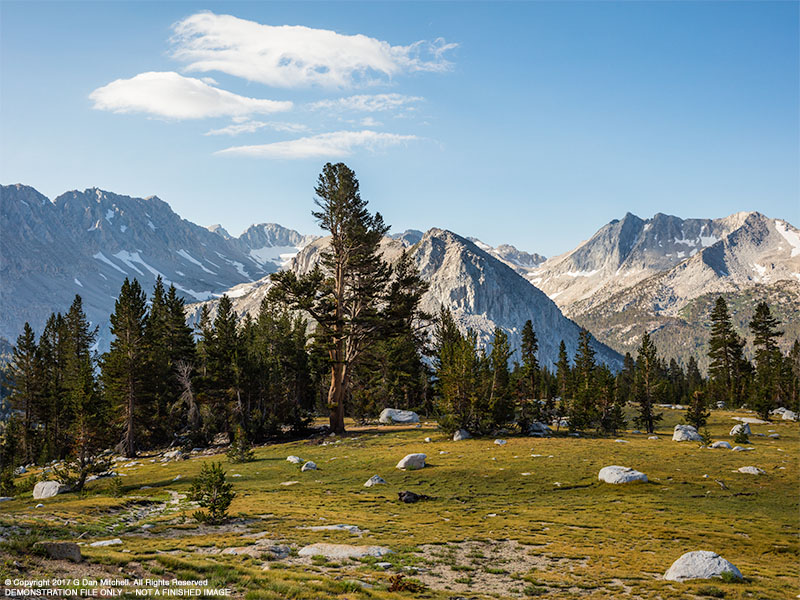
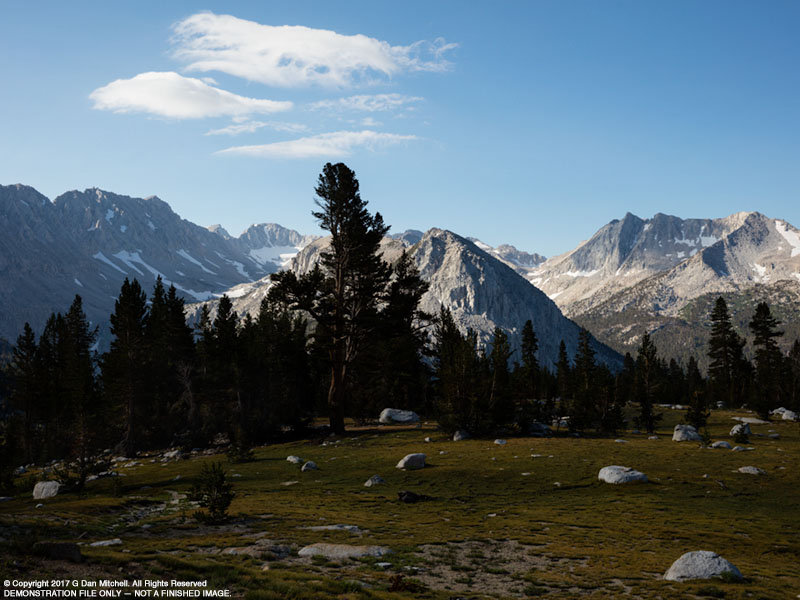
I decided to experiment a bit with this image. What is a photograph, anyway? No photograph is “real” and every photograph offers only a limited and incomplete view of its subject. This image begins as a photograph of some rocks. (The original image appeared at this website previously.) A very close look might reveal the underlying subject, though it is not easy to see. But I had an urge to use it as a starting point for experimentation.
From time to time I have played with altering photographic images more than usual, partly as a way to develop my “chops” and partly because, well, this fascinates me. The immediate inspiration for this one was an online conversation a few days ago that considered how far a photograph can be “pushed.” Years ago I decided to refer to these experiments as “imaginary landscapes,” in part to acknowledge that they forego photographic realism.
G Dan Mitchell is a California photographer and visual opportunist. His book, “California’s Fall Color: A Photographer’s Guide to Autumn in the Sierra” is available from Heyday Books, Amazon, and directly from G Dan Mitchell.
Blog | About | Instagram | Flickr | Facebook | Threads | Post | Email
Links: Articles, Sales and Licensing, my Sierra Nevada Fall Color book, Contact Info.
Scroll down to share comments or questions. (Click post title first if viewing on the home page.)
All media © Copyright G Dan Mitchell and others as indicated. Any use requires advance permission from G Dan Mitchell.